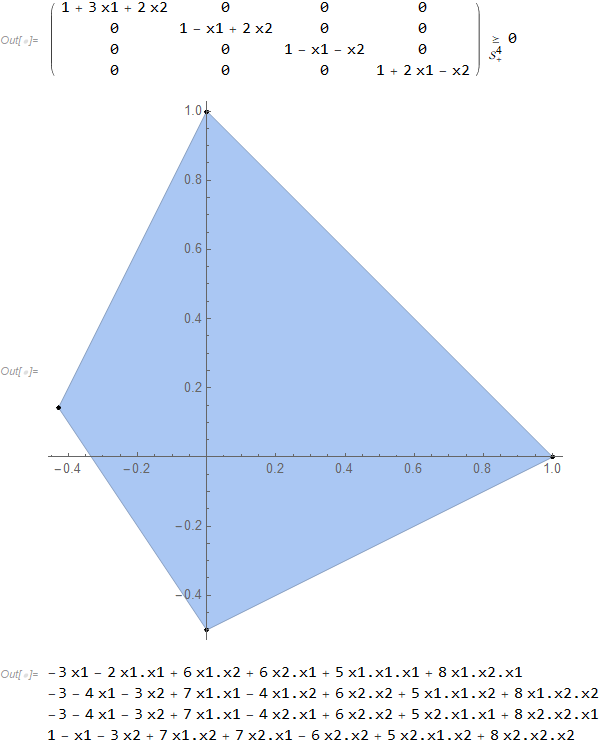
Gröbner basis for the noncommutative ideal which determines the free (noncommutative) extreme points of the free quadrilateral defined by the linear matrix inequality above.
A tuple (x1,x2) of N x N matrices is a free extreme point of this free quadrilateral if and only if (x1,x2) is a member of the free quadrilateral and each of the above polynomials evaluates to zero on (x1,x2).
NCSE
I am the main developer of NCSE (NCSpectrahedronExtreme). NCSE is a Mathematica paclet designed for performing computations with extreme points of free spectrahedra. Examples of computations which can be preformed with NCSE are:
- classification of matrix tuples as a free or classical extreme points of a free spectrahedron.
- representation of an element of a free spectrahedron as a matrix convex combination of free extreme points satisfying a free Caratheodory bound on the number of free extreme points.
- generation and examination of random extreme points of a free spectrahedron.
NCSE is designed to be used with NCAlgebra, a Mathematica paclet for performing symbolic noncommutative computer algebra.
In addition to NCSE, I have contributed to several publicly available user notebooks for NCAlgebra. These notebooks include computation of noncommutative ideals which determine the free extreme points of a given free quadrilateral and computation of convextonic maps between free spectrahedra